One of the great things about a DD-WRT router is that you can do lots of things with it (as well as using it for VPN of course!). If your router has USB slots (as the RT-ACU66U does), then you can plug in a USB hard drive and use it as Network Attached Storage (NAS) - a centralized storage hub that every authorized person on your network can access.
If you'd like to know more about DD-WRT, we'd also recommend reading our huge DD-WRT Guide.
This is great for sharing files or resources in the office, or acting as a centralized media streaming server in the household, so that family members can view or listen to a shared library of movies, music or photos, using any computer, smart phone, smart TV, tablet, or other network connected device.
How to set up NAS storage on your DD-WRT router
For this you will need:
- A DD-WRT router with a USB slot
- An external USB hard drive or USB memory stick (as far as your router and computer are concerned, these are identical)
1. Attach your USB storage to the router and power it up (if needed).
2. Enter your router config page by typing the router IP address (usually http://192.168.1.1/) into your browser address bar. Click on the ‘Services’ tab, and then the ‘USB’ tab.
3. Enable ‘Core USB Support’, ‘USB Storage Support’ and ‘Automatic Drive Mount’. If you have a spare USB port and want to connect a printer for wireless printing, you can enable ‘USB Printer support’ as well. Click ‘Save’ and then ‘Apply Settings’.
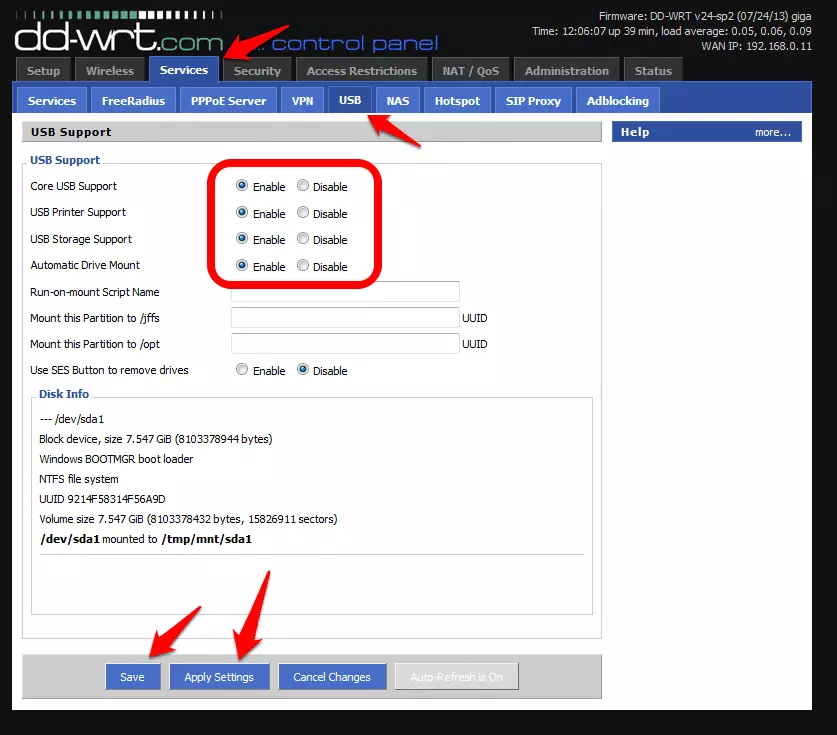
4. Details about your USB storage device should appear in the ‘Disk Info’ section. If they don’t, then re-start the router and come back to this page.
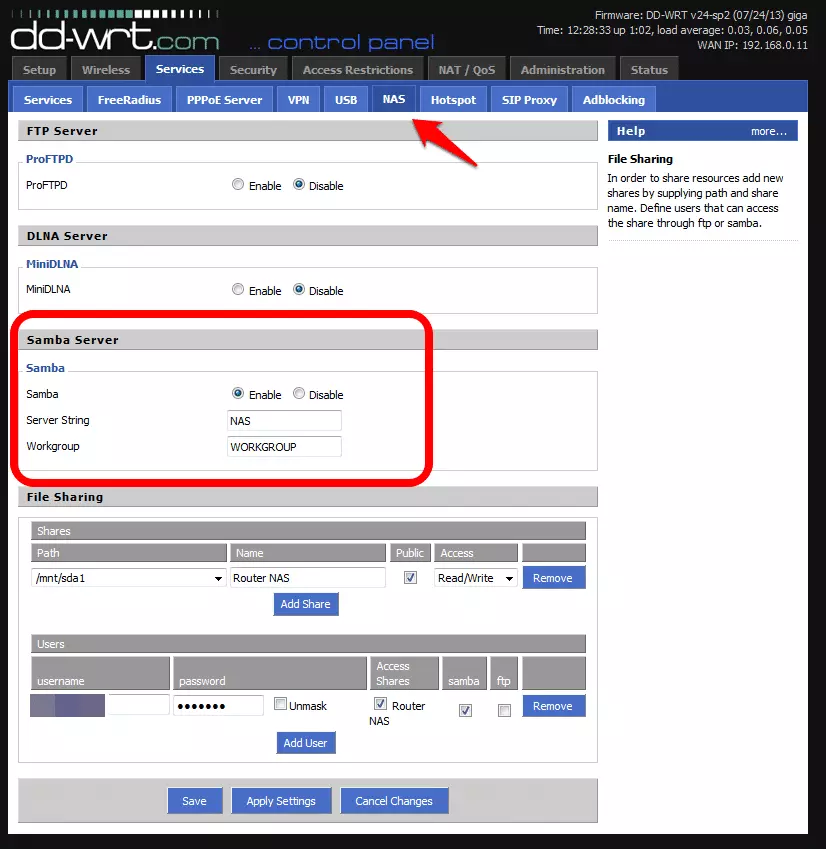
5. Click on the ‘NAS’ tab. We are going to use SAMBA for this, so ‘Enable’ it, choose a Server String (name), and add your Workgroup. To discover or change your workgroup:
- In Windows go to Control Panel -> System
- In OSX go to System Preferences -> Network -> AirPort -> Advanced -> WINS
- In Linux / Ubuntu to install Samba, open up a terminal window and issue the command: sudo apt-get install samba smbfs (you will need to enter your sudo password). Go to the /etc/samba/smb.config file and look for the line 'workgroup = WORKGROUP'.
6. Under ‘File Sharing’, click Add share, select a storage device or device partition from the ‘Path’ dropdown menu, and choose a name for the storage. If you want everyone who joins the network to be able to access the NAS storage then check ‘Public’, and decide whether permission is Read/Write or Read Only.
If you prefer to restrict access to named users then click ‘Add User’ and fill in the details, ensuring that ‘Samba’ is checked. Repeat for each authorized user (or less securely simply share a single User account details with all authorized users).
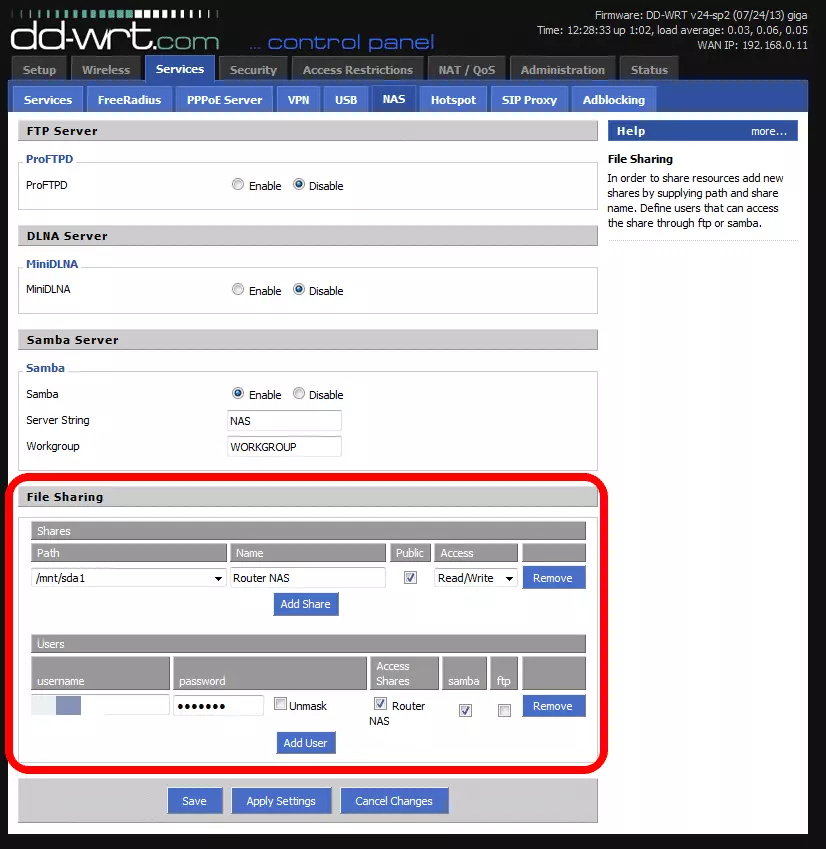
‘Save’ and ‘Apply Settings’
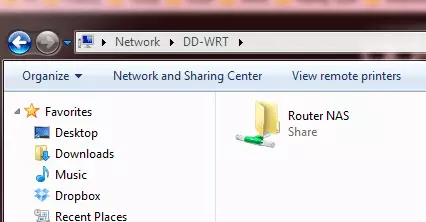
7. Your NAS drive should now be accessible over your Network:
- In Windows go to Start -> Network -> [Router name] -> [drive or partition name]
- In OSX go to File Manager -> Shared pane or Network folder -> -> [Router name] -> [drive or partition name]
- In Linux / Ubuntu follow these instructions.
Here we can see the NAS drive-in Windows
Mobile devices should also be able to access the NAS drive, but the specifics depend on which app you use.
